For any questions:
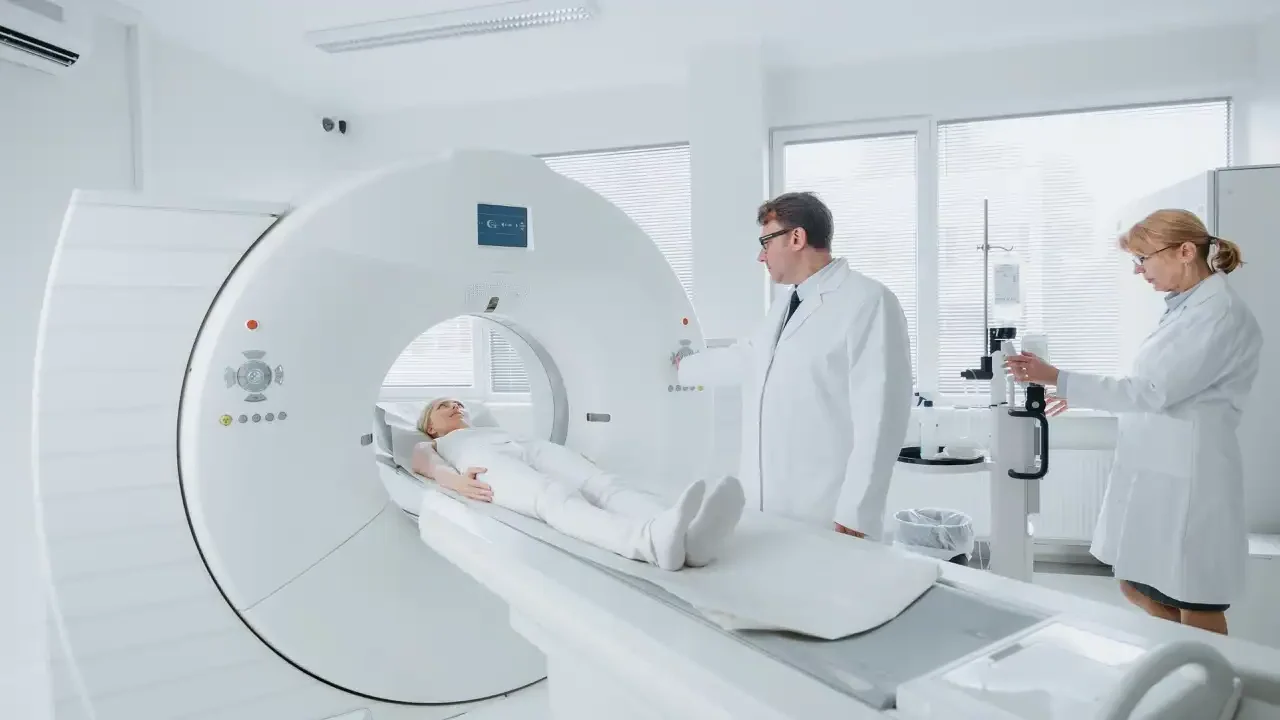
Oncology surgery includes all the surgical procedures required by those suffering from cancer:
Investigation – making a medical assessment in situations in which cancer is suspected
Diagnosis – specifying the type of cancer (biopsy)
Stage – determining the stage of the disease
Treatment – curing or relieving the symptoms of cancer
The surgical treatment of cancer is the result of a multidisciplinary approach: all the specialists involved in cancer diagnosis and treatment participate in choosing the best treatment.
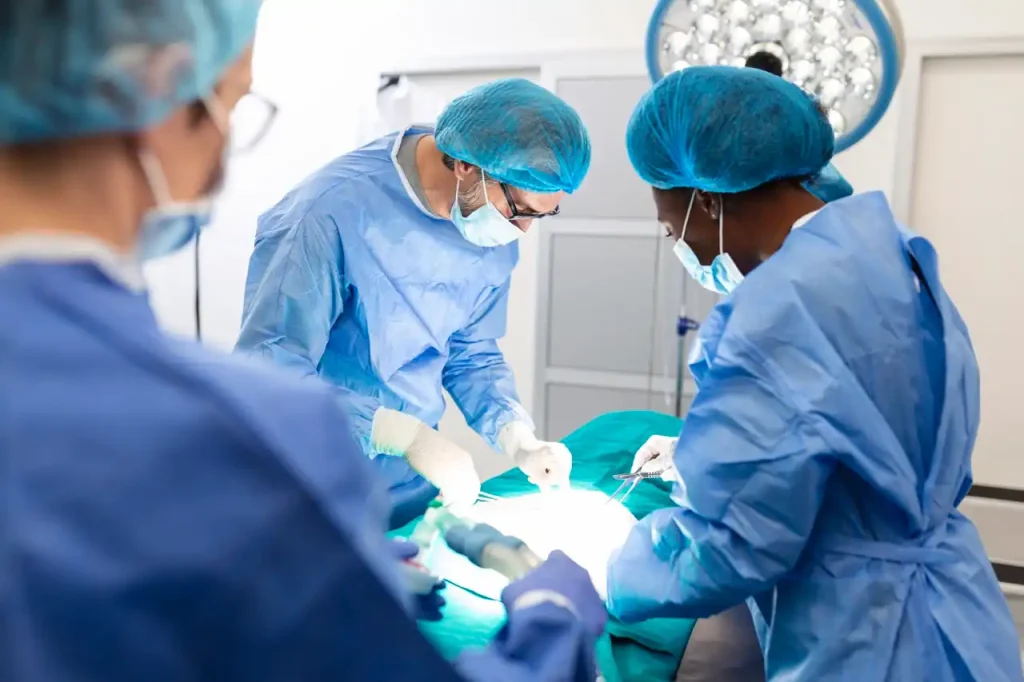
Accordingly, oncology surgeons are part of a multidisciplinary team made up of several professionals. They are all required to have specialized training and expertise in oncology.
Since it is a “local” treatment, surgerive treatment to patients who are obliged to lie still for long periods of time.
Postoperative pain control
Types of oncology surgery
There are various types of oncology surgery depending on the objective of the procedure. They fall under the following categories : Diagnostic surgery, Prophylactic or preventive surgery, Curative surgery, Tumour reduction surgery or surgical cytoreduction, Reconstructive or restorative surgery, Palliative surgery, Surgery for secondary cancers or metastases, Surgery to support treatment.
Surgical techniques
Today, several surgical techniques are used : Conventional open surgery, Endoscopic or minimally invasive surgery, Laser surgery, Robotic surgery.
Preparing for surgery
The following is an overview of preparing for all types of surgery, oncological or otherwise.
The postoperative period
Postoperative care begins at the end of the operation and continues in the recovery room or day surgery room, as appropriate, throughout hospitalization and continues during the return home and recovery period.
To find out more
To obtain more detailed information on surgical oncology and some tips on how to feel better, call the Info-cancer Hotline at 1-800-363-0063 to talk to a nurse or documentalist.
Borrow one or more books on the subject free of charge from our Info-cancer Library (available in French only).